Enhance capacity to report and monitor PHMI/HEDIS quality measures for populations of focus using standardized measurement specifications and a data mapping assessment, and use it to improve quality of care
INTRODUCTION
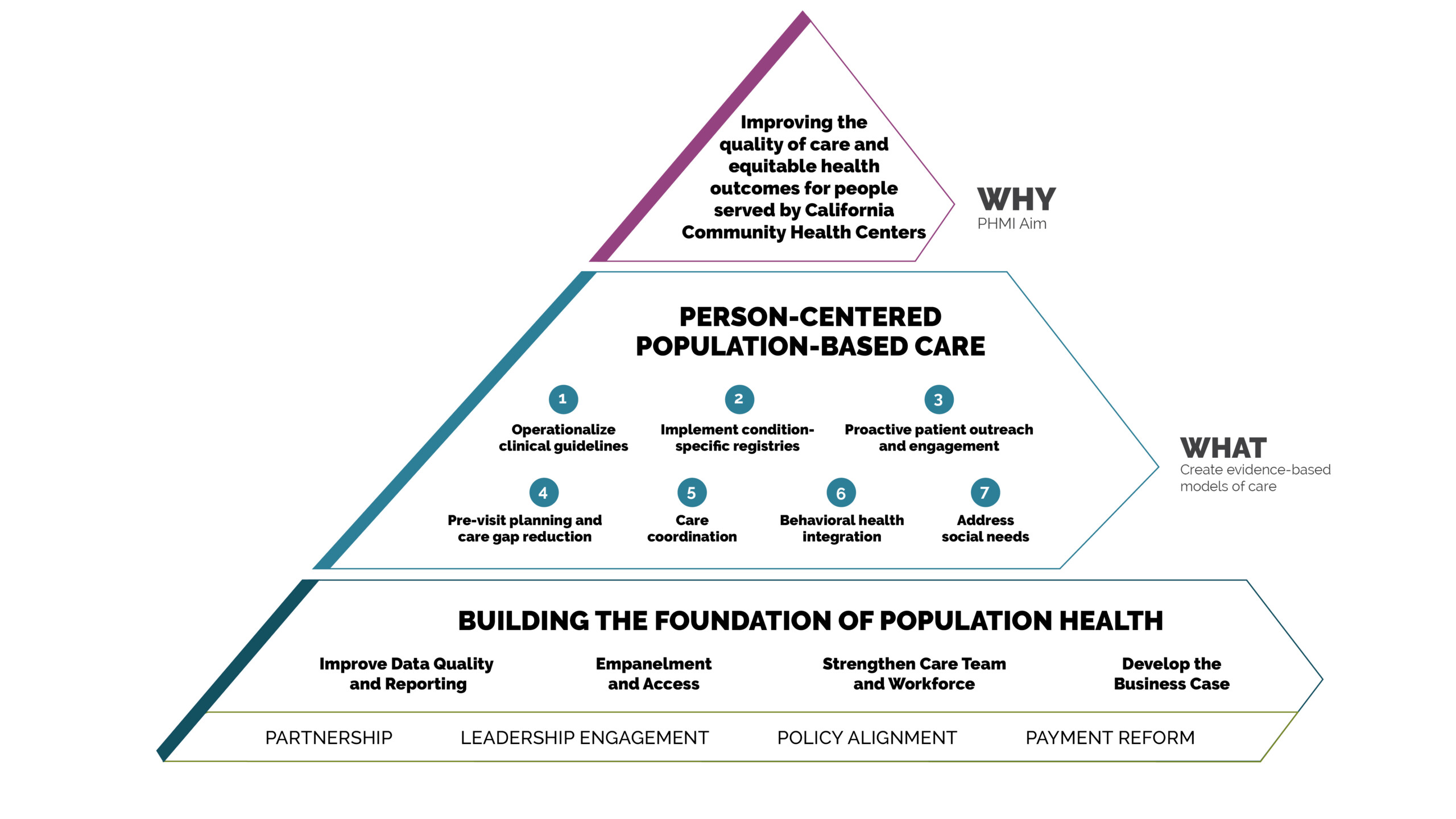
Building the Foundation Implementation Guide Series
WELCOME
Thank you for your commitment to improving the health of Californians by strengthening population health management! Whether you are a community health center (CHC) or another type of primary care practice, this publicly available series of tools and materials is designed to support you in building a foundation for strong population-based care. In this document you will learn about the Population Health Management Initiative (PHMI) and its many partners across the state of California who are working together to support improved care for Medi-Cal members. You’ll learn about:
- The Population Health Management Initiative.
- Where to start with population health management.
- Tools and resources to support organizational change.
- How PHMI efforts can prepare you to succeed with value-based care and California Advancing and Innovating Medi-Cal (CalAIM).
Whether you are just beginning your population health management journey or well on your way, we hope you find these tools and resources helpful.
What is the Population Health Management Initiative?
PHMI is a California partnership of the Department of Health Care Services (DHCS), Kaiser Permanente, and community health centers (CHCs). Together we are advancing population health management capabilities in order to eliminate health disparities and improve the health of people and communities.
Through codesign with CHCs and the support of Kaiser Permanente, PHMI is aligning with CalAIM and Alternative Payment Model 2.0 (APM 2.0) to:
- Focus on shared priority measures and populations, including children, pregnant people, people with behavioral health conditions, and adults living with chronic conditions and preventive care needs.
- Engage resources and expertise to create population health management solutions that work.
- Invest in technology solutions to improve data capabilities.
Why is This Work so Important?
In 2022, nearly half of Californians skipped or postponed some kind of healthcare due to cost. Among those who postponed care, 47% reported their condition worsened as a result.1 Community health centers and primary care practices have been critical leaders in creating access to high quality care, but have been challenged by increasing patient needs and simultaneous staffing and supply shortages in recent years. PHMI partners are providing the resources needed to strengthen CHCs and other primary care practices. With deep investment in a shared data and analytics platform, handson primary care practice coaching and peer learning, and intentional alignment with APM 2.0 payment and CalAIM policy changes, we can come together to improve health outcomes and reduce health disparities.
How was PHMI Designed?
Planning for the initiative began in October 2021 when more than 90 people and organizations across the state came together to contribute to a unified model for population health management that would improve care for Medi-Cal beneficiaries. Partners including CHCs, California Department of Health Care Services (DHCS), Kaiser Permanente, Regional Associations of California, and the California Primary Care Association (CPCA) came together for a series of interactive virtual sessions to create a collaborative vision, think through ideal future experiences for patients and care teams, and brainstorm equity-advancing solutions around healthcare workforce, processes and technology needs.
In addition to the more than 270 proposed solutions that emerged from codesign, PHMI built on a strong body of evidence and best practices for supporting primary care, many of which were developed in California and are now used nationally. The initiative’s developmental work was informed by local institutions, such as University of San Francisco’s Center for Excellence in Primary Care and Stanford’s Clinical Excellence Research Center among many others.
What are PHMI’s Initial Populations of Focus?
The initial PHMI priority populations align with CalAIM and APM 2.0 and include:
- Pregnant people.
- Children.
- Adults with preventive care needs.
- Adults living with chronic conditions.
- People with behavioral health conditions.
Practices participating in PHMI will select a population of focus from this list for their initial population health management work.
What are the Core Quality Measures for PHMI?
The following table outlines PHMI’s populations of focus with their corresponding Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS) quality measures. These measures are directly aligned with APM 2.0 to help CHCs interested in pursuing valuebased pay solutions as they advance equity-based population health improvement.
|
PHMI Populations of Focus |
Measures |
|---|---|
Children |
Child Immunization Status |
|
Well Child Visits in First 30 Months of Life |
|
Pregnant people |
Prenatal and Postpartum Care |
Adults with preventive care needs |
Colorectal Cancer Screening |
Adults living with chronic conditions |
Controlling High Blood Pressure |
|
Comprehensive Diabetes Care |
|
People with behavioral health conditions |
Depression Screening & Follow-Up for Adolescents and Adults |
How does PHMI Advance Equity and Eliminate Health Disparities in California?
One of the primary goals of PHMI and CalAIM is to eliminate health disparities and improve outcomes for Medi-Cal enrollees. The CHCs participating in this initiative were originally selected from regions of the state with some of the most significant health disparities. Together we are working to reduce disparities at a state level by strengthening capacities of participating CHCs to improve health outcomes for their patients in these regions.
PHMI is designed to strengthen health by emphasizing populations of focus where disparities exist (e.g., maternal health outcomes). Health centers will build their foundational capabilities to collect and analyze REAL (race, ethnicity and language) data and social needs data. This foundation will be essential for practices to tailor interventions for subpopulations experiencing disparities. Addressing disparities also requires practices to build structures and approaches to ensure culturally appropriate care teams and outreach to patients. Reducing disparities necessitates collaboration with patients and community organizations to address individual and community-level social factors that influence health improvement.
BUILDING THE FOUNDATION
Implementation Guides
What follows are executive summaries and tools associated with the four “Building the Foundation” implementation guides: Data Quality and Reporting, Empanelment, Care Teams and Workforce, and Business Case. All tools are in the public domain and are available to be used and adapted as needed for your context.
After working through the “Building the Foundation” series of implementation guides (coming October 2023), you will be able to:
Data Quality and Reporting
- Form a data governance and reporting team.
- Produce core quality measures using PHMI/HEDIS specifications.
- Develop and implement a data validation process that identifies gaps and solutions for improving data quality, such as reconciliation with managed care plans.
- Produce quarterly PHMI/HEDIS core quality measures stratified by site, race and ethnicity to identify and reduce disparities and improve performance.
Empanelment
- Identify a panel manager.
- Conduct initial patient assignment and balance supply and demand.
- Implement ongoing panel management by regularly monitoring empanelment reports and making panel adjustments.
Care Teams and Workforce
- Define and establish a core care team incorporating team-based care principles.
- Assure that care teams know their patient panels (applies only if the practice is also working on empanelment or has it in place).
- Assure patients knows their care team.
- Build expanded care team functions that incorporate team-based care principles.
Business Case
- Form a multidisciplinary team to complete the Business Case Tool.
- Complete the Business Case Tool.
- Develop an implementation plan that includes necessary care team functions for population health management and have it approved by leadership.
- Implement the plan.
Who is Most Likely to Use These Guides?
These guides are designed to be helpful as part of an organized quality improvement strategy, with the goal of supporting substantive cultural, technological and process changes that improve population based care. They are designed to be used by practice facilitators, coaches and external consultants who are helping improve care. In addition, enterprising practices can take on this work on their own with internal champions, including quality improvement and program leaders leading the way
Where Do We Start?
The journey to effective population health management isn’t a straight line, however the guides are sequenced to lay a solid foundation from which you can build knowledge and infrastructure to accomplish the next steps in the process. We recommend you start with Data Quality and Reporting, followed by Empanelment, Care Teams and Workforce, and then Business Case. As with any improvement effort, iteration is essential to progress. You may revisit some of these topics repeatedly throughout your population health management journey.
As your team jumps in, teams may find it helpful to begin with an assessment of their current capabilities with regard to population health management.
Take the PhmCAT
The Population Health Management Capabilities Assessment (PhmCAT) helps you set your starting point for this work. If you are one of the community health centers in the first PHMI cohort, you will be taking the PhmCAT four times over the course of the two-and-a-half-year initiative. Even if you are not part of PHMI, consider using the assessment to conduct a gap analysis within your organization, and repeat to monitor progress over time. Additional details about how to use the assessment are available in the overview to the PhmCAT.
Getting Started with Practice Changes
Once you’ve completed the assessment, you will be ready to dive into the implementation guides, each of which provides sequential step-by-step instructions on how to work through a set of key changes. For those who have mastered the basics of population health management, each guide also includes a section called “Going Deeper,” which provides more advanced content, and “On the Horizon,” which discusses promising new directions. We also offer the practical tools you’ll need to do this work effectively and efficiently.
Each guide contains:
- Context on the topic and why it is important.
- Tips on how to use the guide, including prework and how to get started.
- Key step-by-step activities.
- Strategies to advance equity.
- Change management tips.
- Resource considerations.
- Ideas for going deeper.
- What’s on the horizon for primary care.
- Tools and resources to help you implement the work.
The best place to start your population health journey is here!
Check out the implementation guide executive summaries and tools below for the latest science and best practices for population health.

Data Quality and Reporting Guide

Empanelment Guide
Select and implement a methodology to create patient panels and develop continuity reports.

Care Teams and Workforce Guide
Assess current care team roles and functions, identify gaps, and develop and execute a workforce plan.

Business Case Guide
Utilize a business case tool to develop your financial model for population health management sustainability. This tool is currently designed for community health centers and how they are paid, but can be adapted by other practices.
What’s Next?
CHCs participating in the PHMI initiative have access to tailored coaching, peer learning and action networks, online tool sharing, a shared data and analytics platform, and more where insights and learnings will develop. The PHMI team is committed to making as many emergent insights, tools and resources publicly available as possible as the initiative unfolds. This includes learnings to support related population health management initiatives like the Equity Practice Transformation payment program (EPT) from DHCS. We also hope to build coaching expertise that practices outside of the formal PHMI can access as they implement their own population health improvement efforts.
Where Do I Go for More Help?
If you are part of one of our initial 32 community health centers, your practice coach will be your interpreter, guide and facilitator. Reach out to your coach with any questions.
If you are part of Equity and Practice Transformation (EPT), visit the EPT website or contact your managed care plan. Otherwise, please reach out to us at phm_initiative@kp.org.
This is also the best place to share your input and suggestions about ways we can better support your work. We welcome your feedback as we move forward together.
Will the Guides Be Updated in the Future?
Please note this is version one of the implementation guides, and the PHMI team is on this learning and improvement journey with you. The guides are being tested in 2023 and the first half of 2024, and will be revised based on our findings and continue to evolve. Check back or sign up for our PHMI newsletter for quarterly updates.